Balkrishna Rawool
Algebraic Data Types + Pattern Matching = Elegant and readable Java code
#1about 2 minutes
Introducing the 'SEND + MORE = MONEY' puzzle
A cryptarithmetic puzzle is presented where letters represent unique digits in a mathematical equation that must be solved.
#2about 3 minutes
Designing a solver and defining an expression grammar
A high-level solution is designed with a generator and evaluator, based on a grammar that defines expressions as constants, variables, additions, or multiplications.
#3about 4 minutes
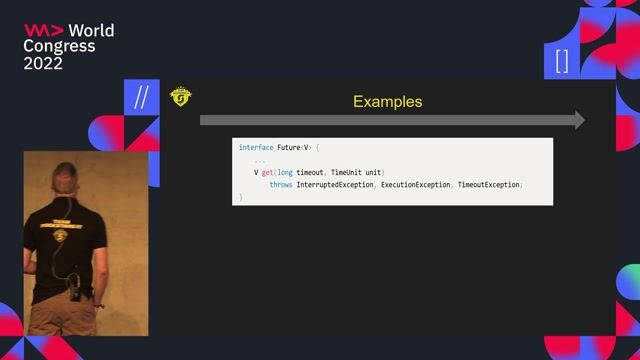
Understanding algebraic data types and pattern matching in Java
Product types are implemented with records and sum types with sealed interfaces, which can then be deconstructed using pattern matching for `instanceof` and `switch`.
#4about 2 minutes
Modeling expressions as an algebraic data type
An expression is modeled as a sum type using a Java sealed interface with record implementations for constant, variable, addition, and multiplication.
#5about 3 minutes
Implementing an evaluation function with pattern matching
A static `evaluate` function uses a pattern matching switch expression to recursively calculate the value of an expression tree, ensuring compile-time safety.
#6about 8 minutes
Building the puzzle solver and constraints
The main puzzle solver logic is built by creating a sealed interface for constraints and using a generator to check all combinations against them.
#7about 4 minutes
Assembling and running the puzzle solution test
A unit test is created to assemble the puzzle's variables, expressions, and constraints, which is then run to find and verify the final solution.
#8about 1 minute
The pattern of data-oriented programming in Java
The combination of algebraic data types for data modeling and pattern matching for behavior is defined as data-oriented programming, a powerful pattern for writing readable code.
Related jobs
Jobs that call for the skills explored in this talk.
Matching moments

03:32 MIN
Applying data-oriented programming principles in Java
Modern Java: This is not your father's Java anymore
02:08 MIN
Refactoring asynchronous code with modern Java features
Using Java 17 latest features in real world projects

17:35 MIN
Major language enhancements from Java 12 to 17
Beam Me Up, Java! Unraveling the Warp-Speed Evolution: A Journey through Java LTS Versions 11 to 21
06:45 MIN
Modeling distinct data states with algebraic data types
Tackling Complexity With Functional Programming And Kotlin
03:12 MIN
Using Java sealed interfaces with records for conciseness
Java Sealed Classes vs. Kotlin Sealed Classes #Slideless

03:00 MIN
Modeling data alternatives using sealed interfaces and records
Data-Oriented Programming - Version 1.1

02:42 MIN
Comparing data-oriented programming to the visitor pattern
Data-Oriented Programming - Version 1.1

05:21 MIN
Leveraging pattern matching for switches and records
Modern Java: This is not your father's Java anymore
Featured Partners
Related Videos
 28:24
28:24Data-Oriented Programming - Version 1.1
Nicolai Parlog
 28:48
28:48Tackling Complexity With Functional Programming And Kotlin
Georg Dresler
 27:39
27:39Modern Java 25
Ron Veen
 38:07
38:07Java Sealed Classes vs. Kotlin Sealed Classes #Slideless
Lothar Schulz
 27:49
27:49Modern Java: This is not your father's Java anymore
Ron Veen
 30:28
30:28Using Java 17 latest features in real world projects
Ron Veen
 45:30
45:30Best of Java 15 and beyond—my favorite features
Michael Inden
 41:37
41:37Java with a Clojure mindset
Dan Lebrero
Related Articles
View all articles.gif?w=240&auto=compress,format)


.gif?w=240&auto=compress,format)
From learning to earning
Jobs that call for the skills explored in this talk.






Joh. Berenberg, Gossler & Co. KG
Kotlin
TypeScript
Kubernetes
Machine Learning
Software Architecture
+1


